Why is object recognition from novel viewpoints facilitated if not the object rotates, but the observer moves around the object? According to the prevailing opinion, “spatial updating” of our mental spatial representation is supposed to be the underlying process. Here, we provide first evidence that challenge this notion, in that dynamic visual cues alone might be sufficient or at least contributing to improved object recognition from novel viewpoints
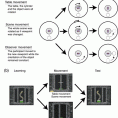
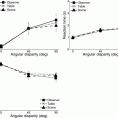
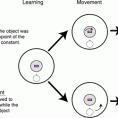
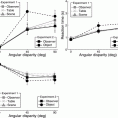
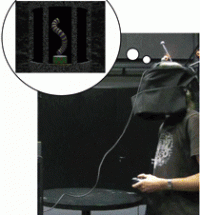
Normally, people have difficulties recognizing objects from novel as compared to learned views, resulting in increased reaction times and errors. Recent studies showed, however, that this “view-dependency” can be reduced or even completely eliminated when novel views result from observer’s movements instead of object movements. This observer movement benefit was previously attributed to extra-retinal (physical motion) cues. In two experiments, we demonstrate that dynamic visual information (that would normally accompany observer’s movements) can provide a similar benefit and thus a potential alternative explanation. Participants performed sequential matching tasks for Shepard-Metzler-like objects presented via head-mounted display. As predicted by the literature, object recognition performance improved when view changes (45° or 90°) resulted from active observer movements around the object instead of object movements. Unexpectedly, however, merely providing dynamic visual information depicting the viewpoint change showed an equal benefit, despite the lack of any extra-retinal/physical self-motion cues. Moreover, visually simulated rotations of the table and hidden target object (table movement condition) yielded similar performance benefits as simulated viewpoint changes (scene movement condition). These findings challenge the prevailing notion that extra-retinal (physical motion) cues are required for facilitating object recognition from novel viewpoints, and highlight the importance of dynamic visual cues, which have previously received little attention.