How can we improve telepresence systems (such as conference robots) so they are not just “zoom on wheels” but actually allow users to feel more present and navigate more easily around remote environments?”
FeetBack: Augmenting Robotic Telepresence with Haptic Feedback on the Feet
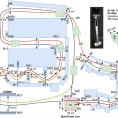
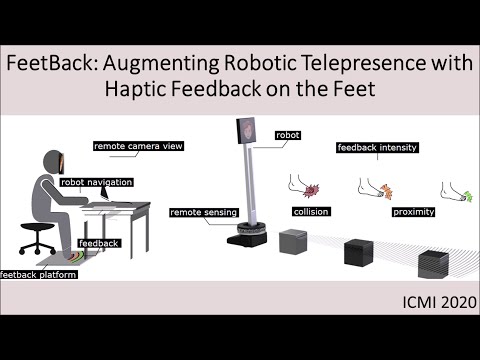
Telepresence robots allow people to participate in remote spaces, yet they can be difficult to manoeuvre with people and obstacles around. We designed a haptic-feedback system called “FeetBack,” which users place their feet in when driving a telepresence robot. When the robot approaches people or obstacles, haptic proximity and collision feedback are provided on the respective sides of the feet, helping inform users about events that are hard to notice through the robot’s camera views. We conducted two studies: one to explore the usage of FeetBack in virtual environments, another focused on real environments. We found that FeetBack can increase spatial presence in simple virtual environments. Users valued the feedback to adjust their behaviour in both types of environments, though it was sometimes too frequent or unneeded for certain situations after a period of time. These results point to the value of foot-based haptic feedback for telepresence robot systems, while also the need to design context-sensitive haptic feedback
Conference presentation at ICMI 2020:

System overview:
Publications
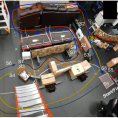
How automatic speed control based on distance affects user behaviours in telepresence robot navigation within dense conference-like environments
Telepresence robots allow users to be spatially and socially present in remote environments. Yet, it can be challenging to remotely operate telepresence robots, especially in dense environments such as academic conferences or workplaces. In this paper, we primarily focus on the effect that a speed control method, which automatically slows the telepresence robot down when getting closer to obstacles, has on user behaviors. In our first user study, participants drove the robot through a static obstacle course with narrow sections. Results indicate that the automatic speed control method significantly decreases the number of collisions. For the second study we designed a more naturalistic, conference-like experimental environment with tasks that require social interaction, and collected subjective responses from the participants when they were asked to navigate through the environment. While about half of the participants preferred automatic speed control because it allowed for smoother and safer navigation, others did not want to be influenced by an automatic mechanism. Overall, the results suggest that automatic speed control simplifies the user interface for telepresence robots in static dense environments, but should be considered as optionally available, especially in situations involving social interactions.
Publications
Geocaching with a Beam: Shared Outdoor Activities through a Telepresence Robot with 360 Degree Viewing
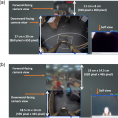
People often enjoy sharing outdoor activities together such as walking and hiking. However, when family and friends are separated by distance it can be difficult if not impossible to share such activities. We explore this design space by investigating the benefits and challenges of using a telepresence robot to support outdoor leisure activities. In our study, participants participated in the outdoor activity of geocaching where one person geocached with the help of a remote partner via a telepresence robot. We compared a wide field of view (WFOV) camera to a 360° camera. Results show the benefits of having a physical embodiment and a sense of immersion with the 360° view. Yet challenges related to a lack of environmental awareness, safety issues, and privacy concerns resulting from bystander interactions. These findings illustrate the need to design telepresence robots with the environment and public in mind to provide an enhanced sensory experience while balancing safety and privacy issues resulting from being amongst the general public.
illustration of geocaching with a telepresence robot