Position:
Professor
Contact:
http://home.inf.h-brs.de/~ekruij2m/
Affiliations:
Faculty of Computer Science & Institute for Visual Computing, Bonn-Rhein-Sieg University of Applied Sciences, Germany
Biography
Projects
1st International Workshop on Standardization in Cybersickness Research
1st International Workshop on Standardization in Cybersickness Research: “Establishing Standards for Cybersickness Measurement and Mitigation: A Community-Driven Approach” Date & time: Monday morning 8am-noon, 21 October 2024 at ISMAR 2024 Location: Redmond room, see ISMAR schedule Join remotely using this Zoom link or check on the ISMAR website for updates (contact us if you don't rec...
VR Sickness Benchmark System
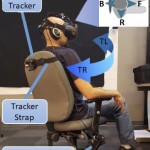
Tackling VR Sickness: A Novel Benchmark System for Assessing Contributing Factors and Mitigation Strategies through Rapid VR Sickness Induction and Recovery Abstract This research introduces a novel VR sickness benchmark system, designed to address the lack of standardized tools for assessing and mitigating VR sickness. It aims to rectify the inconsistencies and limitations prev...
Telepresence
How can we improve telepresence systems (such as conference robots) so they are not just "zoom on wheels" but actually allow users to feel more present and navigate more easily around remote environments?" FeetBack: Augmenting Robotic Telepresence with Haptic Feedback on the Feet Telepresence robots allow people to participate in remote spaces, yet they can be difficult to manoeuvre with people ...
HyperJump flying to combat motion sickness
HyperJumping in Virtual Vancouver: Combating Motion Sickness by Merging Teleporting and Continuous VR Locomotion in an Embodied Hands-Free VR Flying Paradigm Motion sickness, unintuitive navigation, and limited agency are critical issues in VR/XR impeding wide-spread adoption and enjoyable user experiences. To tackle these challenges, we present HyperJump, a novel VR interface merging advantages ...
Concurrent locomotion and interaction in VR
Can more embodied and leaning-based interfaces help support concurrent locomotion and interaction in VR when physical walking isn't feasible? Physical walking is often considered the gold standard for VR travel whenever feasible. However, especially for larger-scale virtual travel the free-space walking areas are typically too small, thus requiring handheld controllers to navigate, which ...
Leaning-based interfaces improve ground-based VR locomotion
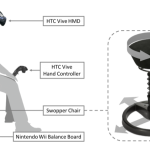
Hand-held VR controllers are widely available and used, however they can contribute to unwanted side-effects, such as increased cybersickness, disorientation, and cognitive load. Here, we show how a leaning-based interfaces ("HeadJoystick") can help improve user experience, usability,and performance in diverse ground-based navigation including three complementary tasks: reach-the-target, follow-th...
Integrating Continuous and Teleporting VR Locomotion into a Seamless "HyperJump" Paradigm
Here we propose a hybrid interface that allows user to seamlessly transition between a slow 'continuous' mode and a fast 'hyperjump' mode. The interface aims to maintain the immersion, presence, accuracy and spatial updating of continuous locomotion while adding the travel efficiency and minimizing the cybersickness. Continuous locomotion in VR provides uninterrupted optical flow, which mimics re...
VR Locomotion Interfaces Survey: How to Move in VR?
There are a multitude of different VR locomotion interfaces out there, all with their own pros and cons. In fact, far too many to all investigate in one behavioural study - so let's ask diverse VR experts for their opinion... Interested in supporting research on VR locomotion interfaces and helping the VR community better understand the pros and cons of different interfaces? We created a surve...
FaceHaptics: Robot Arm based Versatile Facial Haptics for Immersive Environments
Beyond audiovisual cues in VR: Using an HMD-mounted robot arm for versatile facial haptics Abstract: FaceHaptics is a novel haptic display based on a robot arm attached to a head-mounted virtual reality display. It provides localized, multi-directional and movable haptic cues in the form of wind, warmth, moving and single-point touch events and water spray to dedicated parts of the face ...
Embodied & Intuitive Flying for VR, Gaming, and TeleOperation
Flying has been a dream for mankind for millenia - but flying interfaces for VR, gaming, and teleoperation (e.g., drones) typically rely on cumbersome double-joystick/gamepads and do not allow for intuitive and embodied flying experiences. Here, we develop low-cost embodied flying interfaces that adapt leaning-based motion cueing paradigms thus freeing up hands for additional tasks beyond just na...
NaviBoard: Efficiently Navigating Virtual Environments
Here we propose a novel and cost-effective setup of a leaning-based interface ("NaviBoard") that allows people to efficiently navigate virtual environments - with performance levels matching the gold standard of free-space walking, without any increase in motion sickness Abstract Walking has always been the most common locomotion mode for humans in the real world. As a result, it has also been co...
3D User Interfaces Course
Siggraph 2018: 3D User Interfaces for Virtual Reality and Games: 3D Selection, Manipulation, and Spatial Navigation 3-hour Course Presented at Siggraph 2018 In this course, we will take a detailed look at different topics in the field of 3D user interfaces (3DUIs) for Virtual Reality and Gaming. With the advent of Augmented and Virtual Reality in numerous application areas, the need and interest...
Navigation Interface Tutorial
Navigation Interfaces for Virtual Reality and Gaming: Theory and Practice First version held at IEEE VR 2017, Sunday, March 19, 1:30pm - 5:00pm, updated variants of the tutorial will be presented at ACM Chi 2018 (slides) and IEEE VR 2018. At The Spatial Cognition 2018 conference we will present a new tutorial on Spatial Navigation Interfaces for Immersive Environments focusing more on the...
Lean and Elegant Motion Cueing in VR
How do we best design locomotion interfaces for VR that provide "enough" physical motion cues (vestibular/proprioceptive) while still being effective, affordable, compact, and safe? Despite amazing progress in computer graphics and VR displays, most affordable and room-sized VR locomotion interfaces provide only little physical motion cues (e.g., vestibular & proprioceptive cues). To provide...