Position:
Professor
Contact:
ber1 at sfu dot ca
http://www.siat.sfu.ca/faculty/Bernhard-Riecke/
Affiliations:
Full Professor at SFU-SIAT (School of Interactive Arts and Technology)
Associate Member of SFU Cognitive Science Program
Biography
Positions and Affiliations:
- Associate Professor at SFU-SIAT (School of Interactive Arts and Technology)
- Associate Member of SFU Cognitive Science Program
Contact:
ber1 at sfu dot ca
SIAT homepage:
Brief Biography
I am a psycho-physicist and Cognitive Scientist who’s excited about studying how humans orient in virtual and real environments. I received my PhD in Physics from the Tübingen University in Germany and researched for a decade in the Virtual Reality group of the Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics in Germany. After a post-doc in Psychology at Vanderbilt University I joined the School of Interactive Arts & Technology of Simon Fraser University as an assistant professor in 2008. My research approach combines fundamental scientific research with an applied perspective of improving human-computer interaction.
I combine multi-disciplinary research approaches and immersive virtual environments to investigate what constitutes effective, robust, embodied and intuitive human spatial cognition, orientation and behaviour (and many other things as you can see on the projects pages). This fundamental knowledge is used to guide the design of novel, more effective human-computer interfaces and interaction paradigms that enable similar processes in computer-mediated environments like virtual reality (VR) and multi-media. These improved interfaces can then enable and inspire further research, both fundamental and applied.
Supervision
Teaching
Publications
- see also my google scholar page
- my ACM publications can be downloaded here.
- supervised theses
Research Interests
My research interests include:
- Human multi-modal spatial cognition, spatial orientation, spatial updating, and navigation
- Enabling robust and effortless spatial orientation in virtual environments
- Self-motion perception, illusions (“vection”), and simulation; Multi-modal contributions and interactions
- Multi-modal cue integration: Experimentation and theoretical modeling
- Design and iterative evaluation and improvement of perceptually oriented, multi-modal human-computer interfaces and human-centered, effective virtual reality simulations
- Immersion and presence
- Multi-modal, interactive art/dance performances
- and more…
Please see my TEDxEastVan TEDx talk and the diverse research topics and interests for an overview of the different projects and our vision on how we could use the increasing potential of immersive VR (combined with other technologies and approaches, including biosensing) to create meaningful positive experiences.
Could Virtual Reality make us more human? | Bernhard Riecke | TEDxEastVan
Below is a short (older) intro video explaining my overall research agenda and vision for the iSpace lab. See the Vision subpage for details.
Interested in Joining the iSpace Team?
I’m currently looking for bright and motivated PhD students to join our iSpace lab. See the Contact & Join Us subpage for details.
Projects
Beyond the Screen: Combating Cybersickness in Virtual Reality
This research delves into the pervasive issue of cybersickness, a major hurdle to widespread VR adoption. By gathering insights from a diverse group of VR experts, we identify the key factors contributing to motion sickness in virtual environments (aka cybersickness) and offer actionable strategies for developers, content creators, and researchers to build more comfortable and accessible VR experi…
Who Defines Embodiment? Cultural Bias in Interoceptive Wellness Technologies
If interoception is culturally learned rather than biologically universal, how should we design for this variability? Interoception—the perception of internal bodily states such as heartbeat, hunger, and emotion—is foundational to well-being. Despite its significance in wellness technologies within Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), existing designs often impose a universalized model of bo…
Compassionate Connection Oasis VR Toolkit (ccOasisVR)
Empowering Emerging Adults through Compassion and Enhanced Social Connection: Co-creating a Compassionate Connection Oasis VR Toolkit (ccOasisVR) Emerging adulthood (18−25) is a critical developmental phase, a tumultuous transition marked by heightened distress, and, unfortunately, a decreased likelihood that Emerging Adults (EAs) will seek support. The COVID-19 pandemic further exposed the urge…
Sensorium
This mixed-methods study investigates how real versus sham visual biofeedback influences subjective and physiological relaxation, self-connection, body awareness, flow, and self-transcendence within Sensorium 1.5 — an individual, immersive installation combining body-scan meditation, ambient sound, and HRV-responsive LED lighting. Fifty participants will experience both real and sham feedback in…
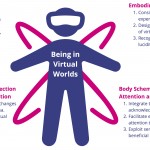
Being in Virtual Worlds
Being in Virtual Worlds: How Interaction, Environment, and Touch Shape Embodiment in Immersive Experiences Embodiment is an everyday experience that typically goes unnoticed. While we often take it for granted, with the adoption of virtual reality (VR) technology, embodiment in virtual bodies and worlds has become an important consideration for designers of immersive experiences. To date, the VR …
HemisFear
HemisFear: A Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy Prototype Driven by Cross-Cultural Understanding of Dog Phobia Can virtual reality turn your terror of a barking stray into calm curiosity? HemisFear’s culturally attuned exposure therapy confronts dog phobias in both suburban backyards and bustling Indian streets, letting you practice handling real-life triggers with the safety of VR. Cynophobia, …
BRieFLY - A meditative VR experience
Breathe, connect, and watch fireflies respond to your touch and breath BRieFLY is an exploratory VR prototype combining mindful breathing with playful interaction. This 6-minute meditative experience immerses users in a mixed reality environment where shimmering fireflies dynamically respond to their movements, as illustrated in the video below. The session begins with a 3-minute narrated b…
VR That Doesn’t Make You Sick: Understanding & Mitigating Cybersickness
Cybersickness remains a persistent challenge in VR/XR, hindering user experience and adoption. This course bridges research and industry, equipping developers, designers, and researchers with science-backed strategies to mitigate cybersickness through optimized locomotion, interaction, and environment design. Engage with case studies and activities to create more comfortable, accessible VR/XR expe…
Unleashing AI in the Classroom
How can AI tools like ChatGPT transform creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking in interdisciplinary education? And what are the risks of over-relying on AI tools in education, and how can students and educators navigate these challenges? How do students feel about using AI tools in their learning? What did they learn, and what would they do differently next time? Lessons Learned from Un…
Cybersickness Survey: Key Factors and Prevention/Reduction Strategies
Welcome to our research project on VR-induced motion sickness (aka cybersickness). We are exploring the factors that cause dizziness and nausea while using VR to make virtual reality experiences more comfortable for everyone — join our study today and be a part of research on combating cybersickness! Who Can Participate? We are looking for individuals who: Have over two years of experience…
Cybersickness & Benchmarking Tutorial at ISMAR 2024
Half-day tutorial at ISMAR 2024 on “Cybersickness: Understanding the Challenge and Building Solutions with Standardized Benchmarks” Join us for an in-depth exploration of cybersickness, a persistent challenge in virtual reality (VR). In this tutorial, we’ll delve into the causes and effects of cybersickness, drawing on the latest research and theories. We’ll…
1st International Workshop on Standardization in Cybersickness Research
1st International Workshop on Standardization in Cybersickness Research: “Establishing Standards for Cybersickness Measurement and Mitigation: A Community-Driven Approach” Date & time: Monday morning 8am-noon, 21 October 2024 at ISMAR 2024 Location: Redmond room, see ISMAR schedule Join remotely using this Zoom link or check on the ISMAR website for updates (contact us if you don’t rec…
Pathways to flourishing
Leveraging Virtual Reality for cultivating compassion, resilience, social connectedness, and healthy habits in emerging adults facing chronic health challenges About half of youths with chronic physical conditions develop anxiety and/or depression, causing significant distress and disruption within their lives over many years. This underscores their need for well-being tools– particularly ones t…
Awedyssey: VR for promoting and enhancing well-being
We are investigating and creating a new virtual reality (VR) experience, ‘Awedyssey’, for the promotion and enhancement of well-being. Today, digital technology pervasively intersects with our daily lives, and VR stands out as a digital tool capable of fostering positive emotion like awe, self-transcendence, and authentic social connection. Connecting with nature is very important for our mental…
VR Sickness Benchmark System
Tackling VR Sickness: A Novel Benchmark System for Assessing Contributing Factors and Mitigation Strategies through Rapid VR Sickness Induction and Recovery Abstract This research introduces a novel VR sickness benchmark system, designed to address the lack of standardized tools for assessing and mitigating VR sickness. It aims to rectify the inconsistencies and limitations prev…
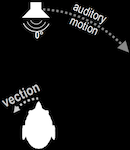
Multisensory Contributions Illusory Self-Motion (Vection)
Beyond the Eye: Multisensory Contributions to the Sensation of Illusory Self-Motion (Vection) Abstract Vection is typically defined as the embodied illusion of self-motion in the absence of real physical movement through space. Vection can occur in real-life situations (e.g., ‘train illusion’) and in virtual environments and simulators. The vast majority of vection research focuses on vectio…
InExChange
InExChange: Fostering Genuine Social Connection through Embodied Breath Sharing in Mixed Reality InExChange is an interactive mixed reality experience centering around an inflatable vest which conveys a physical sense of shared breathing on the diaphragm between two or more participants. The experience is composed of three acts in which the participants’ breaths are transformed into metapho…
Designing with Biosignals Workshop at ACM DIS 2023
Designing with Biosignals: Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Directions for Integrating Physiological Signals in Human-Computer Interaction ABSTRACT Biosensing technologies are a rapidly increasing presence in our daily lives. These sensor-based technologies measure physiological processes including heart rate, breathing, skin conductance, brain activity and more. Researchers are exploring…
ETC - Embodied Telepresent Connection
Embodied Telepresent Connection (ETC): Exploring Virtual Social Touch Through Pseudohaptics ETC (Embodied Telepresent Connection) is an artistic VR project exploring ways of eliciting a feeling of embodied connection telepresently through pseudohaptics. This project emerged during the beginning of COVID-19-related lockdowns when our social interactions began to inhabit nearly exclusively virtual …
Virtual Earthgazing
During months-long missions, Astronauts experience various aspects of social isolation and confinement. Our main aim is to study the feasibility of a virtual reality sensory stimulation augmentation called Virtual Earthgazing (VE). The VE experience is designed to elicit an “overview effect” of the Earth and induce the feeling of awe, which has been shown to expand time perception, increase e…
Flow
Flow is a prototype of a real-time interactive installation with Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) technology, aimed at evoking social connection through bio-signal sharing. The Muse™ headband would stream user’s EEG (brain wave) data and PPG (breathing) data into Unity 3D engine using LSL (Lab Streaming Layer). The generated visualization interact subtly with the participant’s breathing pattern…
Synedelica
Reality — Reimagined Synedelica reimagines what is possible with immersive technology, providing a new perspective on reality. In this synesthetic mixed reality experience, visuals of the real world are modulated by sound, attuning immersants to the beauty hidden in the seemingly mundane. Synedelica shows the world in a new light, rekindling childlike wonder and encouraging exploration. …
Autoethnographic Close Reading of Self-transcendent VR Experiences
Sipping the Virtual Elixir: An autoethnographic close reading of Ayahuasca Kosmik Journey a self-transcendent virtual experience. Recently self-transcendent experiences are gaining interest in the research community because of their ability to support wellbeing. Experiences of self-transcendence can be transformative, leading to a diminishment of self/ego and the feeling of unity with n…
Novel Cybersickness Measures and Countermeasures BoF
Novel Cybersickness Measures and Countermeasures: Birds of a Feather session at SIGGRAPH 2022 Interested in connecting & joining? If you’re interested in connecting to others engaged or interested in the Novel Cybersickness Measures and Countermeasures, you could join our online interactive Birds of a Feather session at Siggraph 2022, on Fri Aug 05, 10 am-11:30 am Log in through h…
Telepresence
How can we improve telepresence systems (such as conference robots) so they are not just “zoom on wheels” but actually allow users to feel more present and navigate more easily around remote environments?” FeetBack: Augmenting Robotic Telepresence with Haptic Feedback on the Feet Telepresence robots allow people to participate in remote spaces, yet they can be difficult to manoeuvre with people …
HyperJump flying to combat motion sickness
HyperJumping in Virtual Vancouver: Combating Motion Sickness by Merging Teleporting and Continuous VR Locomotion in an Embodied Hands-Free VR Flying Paradigm Motion sickness, unintuitive navigation, and limited agency are critical issues in VR/XR impeding wide-spread adoption and enjoyable user experiences. To tackle these challenges, we present HyperJump, a novel VR interface merging advantages …
Design Strategies for Genuine Connection
There is a prominent interest in the potential of technology for mediating social connection, with a wealth of systems designed to foster the feeling of connection between strangers, friends, and family. In this project, we are exploring this design landscape to derive a transitional definition of mediated genuine connection and design strategies employed by artists and designers to support the f…
Concurrent locomotion and interaction in VR
Can more embodied and leaning-based interfaces help support concurrent locomotion and interaction in VR when physical walking isn’t feasible? Physical walking is often considered the gold standard for VR travel whenever feasible. However, especially for larger-scale virtual travel the free-space walking areas are typically too small, thus requiring handheld controllers to navigate, which …
Star-Stuff: a way for the universe to know itself
Available on Oculus AppLab at https://www.oculus.com/experiences/quest/3367089710082568/ Inspired by Carl Sagan, Star-Stuff: a way for the universe to know itself is an immersive experience created to remind immersants of their fundamental connection to humanity and the Universe. This hybrid VR artwork brings two people together remotely or in a co-present installation. In both cases, the …
SIRIUS - Virtual Earthgazing to mitigate effects of sensory isolation
SIRIUS (Scientific International Research in Unique Terrestrial Station) is a series of on-land isolation experiments modelling long-term spaceflight in order to assess the psychophysiological effects of isolation on a crew and prepare for long-duration spaceflights, such as a trip to Mars. An 8-month-long isolation study commenced in Moscow on Nov 4th, 2021, where a crew of 6 people (from Roscosm…
Leaning-based interfaces improve ground-based VR locomotion
Hand-held VR controllers are widely available and used, however they can contribute to unwanted side-effects, such as increased cybersickness, disorientation, and cognitive load. Here, we show how a leaning-based interfaces (“HeadJoystick”) can help improve user experience, usability,and performance in diverse ground-based navigation including three complementary tasks: reach-the-target, follow-th…
Virtual Transcendent Dream
Flying dreams have the potential to evoke a feeling of empowerment (or self-efficacy, confidence in our ability to succeed) and self-transcendent experience (STE), which have been shown to contribute to an individual’s overall well-being. However, these exceptional dreaming experiences remain difficult to induce at will. Inspired by the potential of Virtual Reality (VR) to support profound emoti…
Breath of Light
One must first come to know, through observing oneself — just what one does with breathing. — Elsa Gindler Breath of light is a generative interactive installation, exhibited at the 13th Shanghai Biennale. The installation aims to foster a feeling of connection and awareness through the process of breathing synchronization. Each of the two participants generates their own light with their breat…
Integrating Continuous and Teleporting VR Locomotion into a Seamless "HyperJump" Paradigm
Here we propose a hybrid interface that allows user to seamlessly transition between a slow ‘continuous’ mode and a fast ‘hyperjump’ mode. The interface aims to maintain the immersion, presence, accuracy and spatial updating of continuous locomotion while adding the travel efficiency and minimizing the cybersickness. Continuous locomotion in VR provides uninterrupted optical flow, which mimics re…
VR Locomotion Interfaces Survey: How to Move in VR?
There are a multitude of different VR locomotion interfaces out there, all with their own pros and cons. In fact, far too many to all investigate in one behavioural study — so let’s ask diverse VR experts for their opinion… Interested in supporting research on VR locomotion interfaces and helping the VR community better understand the pros and cons of different interfaces? We created a surve…
FaceHaptics: Robot Arm based Versatile Facial Haptics for Immersive Environments
Beyond audiovisual cues in VR: Using an HMD-mounted robot arm for versatile facial haptics Abstract: FaceHaptics is a novel haptic display based on a robot arm attached to a head-mounted virtual reality display. It provides localized, multi-directional and movable haptic cues in the form of wind, warmth, moving and single-point touch events and water spray to dedicated parts of the face …
BioSpaceVR
Experience space like never before: An awe-inspiring VR experience that takes place in space where the Sun and stars react to biosensors. BioSpaceVR seeks to provide a virtual self-transcendent experience. Self-transcendent experiences are characterized by the feeling of unity with others and the world. Our project is a bio-responsive VR experience that creates an almost childlike experience of …
Immersive Installation for Creative Expression and Public Performance: Transcending Perception
Artist Statement Transcending Perception is an interactive Virtual Reality (VR) installation developed by John Desnoyers-Stewart that allows participants to collaborate in the creative, improvisational production of multisensory experiences. Bodies and space are transformed into instruments which translate presence into performance. This installation reminds participants that they are cre…
Body RemiXer
Extending Bodies to Stimulate Social Connection in an Immersive Installation Body RemiXer connects bodies through movement. It is an experiential projection based Virtual Reality installation that explores novel forms of embodied interaction between multiple participants where their bodies mix into a shared embodied representation producing a playful interaction that aims to support the feeling o…
Lucid Loop: A Virtual Deep Learning Biofeedback System for Lucid Dreaming Practice
Can VR and neurofeedback deep learning art help enhance attention and lucid dreaming practice? Lucid dreaming, knowing one is dreaming while dreaming, is an important tool for exploring consciousness and bringing awareness to different aspects of life. We created a system called Lucid Loop: a virtual reality experience where one can practice lucid awareness via neurofeedback. Visuals are creativ…
Connecting through JeL – bio-responsive VR for interpersonal synchronization
Can a bio-responsive generative art installation foster interpersonal synchronization and connection? JeL is a bio-responsive, immersive, interactive, generative art installation designed to encourage physiological synchronization between the immersants. In this project, we will be exploring how novel forms of interaction can be included in immersive technology to foster the feeling of connection…
Embodied & Intuitive Flying for VR, Gaming, and TeleOperation
Flying has been a dream for mankind for millenia — but flying interfaces for VR, gaming, and teleoperation (e.g., drones) typically rely on cumbersome double-joystick/gamepads and do not allow for intuitive and embodied flying experiences. Here, we develop low-cost embodied flying interfaces that adapt leaning-based motion cueing paradigms thus freeing up hands for additional tasks beyond just na…
NaviBoard: Efficiently Navigating Virtual Environments
Here we propose a novel and cost-effective setup of a leaning-based interface (“NaviBoard”) that allows people to efficiently navigate virtual environments — with performance levels matching the gold standard of free-space walking, without any increase in motion sickness Abstract Walking has always been the most common locomotion mode for humans in the real world. As a result, it has also been co…
3D User Interfaces Course
Siggraph 2018: 3D User Interfaces for Virtual Reality and Games: 3D Selection, Manipulation, and Spatial Navigation 3-hour Course Presented at Siggraph 2018 In this course, we will take a detailed look at different topics in the field of 3D user interfaces (3DUIs) for Virtual Reality and Gaming. With the advent of Augmented and Virtual Reality in numerous application areas, the need and interest…
VR/MR/AR 4 Good: Creating with a Purpose
Interested in connecting & joining? If you’re interested in connecting to others engaged or interested in the xR4Good field, you could join the xR4Good facebook group, or fill out this online signup sheet and state what you’re interested in Introduction Over the past five years, we have seen awareness and creation of Virtual, Mixed, and Augmented Reality (VR/MR/AR or, the ‘immersive realit…
Connected through "AWE": creating immersive experiences for social connection
Do you get enough “awe” in your life? In our busy day-to-day lives, we often take our experiences for granted. While we have the technology to connect with one another, like smart phones, we don’t necessarily get outside with nature, or stargaze. Such activities may consist of common awe-inspiring moments, and we now understand that feeling awe is associated with all sorts of social and well…
Navigation Interface Tutorial
Navigation Interfaces for Virtual Reality and Gaming: Theory and Practice First version held at IEEE VR 2017, Sunday, March 19, 1:30pm — 5:00pm, updated variants of the tutorial will be presented at ACM Chi 2018 (slides) and IEEE VR 2018. At The Spatial Cognition 2018 conference we will present a new tutorial on Spatial Navigation Interfaces for Immersive Environments focusing more on the…
Gamified Research
Gamifying Research — Researchifying Games While traditional experimental paradigms offer tight stimulus control and repeatability, then tend to be a bit boring and removed from many real-world situations, which can limit real-world transferability of results. How can we bring together the methodological strenghs of research with the intrinsic motivation of playfulness and gaming? The …
Navigational Search in VR: Do Reference Frames Help?
Would the rectangular reference frame of a CAVE help to reduce disorientation and improve navigation performance in VR? Here, we show that simply providing the rectangular reference frame of a room (as a simple wireframe cuboid), but not a CAVE improved navigational search performance. Despite recent advances in virtual reality, locomotion in a virtual environment is still restricted becau…
Virtual Earthgazing - towards an overview effect in Virtual Reality
How can we use immersive VR to give people pivotal positive experiences without having to send them out into space? “We went to the Moon as technicians, we returned as humanitarians” reflected Edgar Mitchell after his space flight. This describes the overview effect – a profound awe-inspiring experience of seeing Earth from space resulting in a cognitive shift in worldview, le…
Lean and Elegant Motion Cueing in VR
How do we best design locomotion interfaces for VR that provide “enough” physical motion cues (vestibular/proprioceptive) while still being effective, affordable, compact, and safe? Despite amazing progress in computer graphics and VR displays, most affordable and room-sized VR locomotion interfaces provide only little physical motion cues (e.g., vestibular & proprioceptive cues). To provide…
Pulse Breath Water
Pulse Breath Water is an immersive virtual environment manipulated by the pulse of a participant’s breath that provokes and challenges the interaction between a user and the substantial element of the environment: water. The system “senses” the participant, while the participant’s breathing feeds the system. The process is a symbiotic play between internal human processes [biosensing t…
Lost Spirit
Flight after death: Lost Spirit is an experiential-based Virtual Reality (VR) game whereby the player is transported into the spirit world as they take flight to the afterlife. Experience flight, weightlessness, and wonder. In Lost Spirit, you are stuck in the limbo — a world between the living and the dead. You will drift and fly through different environments, each corresponding to different…
Immersive & Embodied Teleoperation Interfaces
Developing virtual interfaces for embodied tele-operation and locomotion. How can we best design and implement an embodied telepresence system for tele-robotics, so we can safely explore remote, hard-to-reach, or potentially hazardous areas or situations? The goal of the “TeleSpider” project is to design and implement a telepresence system where users can remotely operate a robotic spid…
Biofeedback in VR - SOLAR
Resonance in Virtual Environments: hacking biofeedback for altering user’s affective states How can we combine immersive virtual environments (VE) with biofeedback and gamification to foster relaxation, de-stressing and meditative states? That is, instead of increasing sensory overload, can we use the immersive and affective potential of VE and gamification to assist especially novice meditato…
Motion Seats for VR
Using motion seats for enhancing locomotion and immersion in VR How can we provide a “moving experience” through VR without having to use a full-scale motion platform? Could a compact and relatively low-cost “motion seat” provide some of the same benefits, thus reducing cost, complexity, space & safety requirements? Despite considerable advances in Simulation and Virtual Real…
VR in Architecture Design & Review
How can we use immersive Virtual Reality and embodied locomotion interfaces to to design more cost– and space-efficient solutions for effective presentation and communication of architectural designs and ideas? Our overall goal is to iteratively design and evaluate a novel embodied VR system that enables users to quickly, intuitively, and precisely position their virtual viewpoint in 3D space…
Transition into VR: TransLocation
How can we ease users’ transition from the real surroundings into the virtual world? Many of today’s virtual reality (VR) setups are very much focused on technical aspects rather then the benefits of a coherent user experience. This work explores the idea of enhancing the VR experience with a transition phase. On a physical level, this transition offers the user a meaningful metaphor for en…
Cross-Disciplinary 'Immersion' Framework
Describing media as ‘immersive’ is ambiguous. From debilitating addiction to therapeutic relief, media engagement holds a clear duality in its effect on humanity… Without an interdisciplinary characterization of “immersion”, why do we allow this concept to be so readily invoked in discussions of books, visual art, video games, virtual reality systems and more? While “immersion” into tradit…
The Tabletop Makerspace
The tabletop Makerspace was a Mitacs internship project conducted in collaboration with Science World. A set of classroom tools was developed to support ‘Maker’ activities at the museum. The tools included a home-built 3D printer and a set of electronics kits for working with the Arduino microcontroller. An introduction to electronics workshop was developed with local makers and Science World …
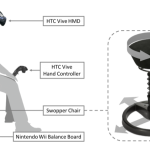
Gyroxus Gaming Chair for Motion Cueing in VR
Can self-motion perception in virtual reality (VR) be enhanced by providing affordable, user-powered minimal motion cueing? Introduction & Motivation: Can self-motion perception in virtual reality (VR) be enhanced by providing affordable, user-powered minimal motion cueing? To investigate this, we compared the effect of different interaction and motion paradigms on onset latency and intensi…
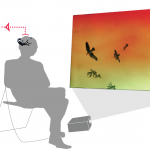
Embodied Self-Motion Illusions in VR
How can we provide humans with a believable sensation of being in and moving through computer-generated environments (like VR, computer games, or movies) without the need for costly and cumbersome motion platforms or large free-space walking areas? That is, how can we “cheat intelligently” by providing a compelling, embodied self-motion illusion (“vection”) without the need for full physical mo…
Dynamic Visual Cues for Spatial Updating
Why is object recognition from novel viewpoints facilitated if not the object rotates, but the observer moves around the object? According to the prevailing opinion, “spatial updating” of our mental spatial representation is supposed to be the underlying process. Here, we provide first evidence that challenge this notion, in that dynamic visual cues alone might be sufficient or at least contrib…
Navigational Search in VR: Do we need to walk?
Do we need full physical motions for effective navigation through Virtual Environments? Recent results suggest that translations might not be as important as previously believed, which could enable us to reduce overall simulation effort and cost Physical rotations and translations are the basic constituents of navigation behavior, yet there is mixed evidence about their relative importance for co…
Spatial Cognition in VR vs. real world
Comparing spatial perception/cognition in real versus immersive virtual environments: it doesn’t compare! Virtual reality (VR) is increasingly used in psychological research and applications – but does VR really afford natural human spatial perception/cognition, which is a prerequisite for effective spatial behavior? Using judgment of relative direction (JRD) tasks, Riecke & McNamara (Psychonom…
iSpaceMecha
Collaboration between the iSpace lab at SIAT and Mechatronics Undergraduate Interns to design and build a unique, virtual reality multi-modal motion simulator The iSpace program is centered on investigating what constitutes effective, robust, and intuitive human spatial orientation and behaviour. This fundamental knowledge will be applied to design novel, more effective human-computer interfaces …
Path Integration in 3D
Switching Spatial Reference Frames for Yaw and Pitch Navigation: We’re used to navigating on the ground plane, and have developed specific strategies to do so. How do these change if we move in a vertical plane (roller-coaster-like, including head over heels motions)? Can we still maintain orientation and remember where we came from, even though such upwards or downwards (pitch) motions are less …
Auditory Navigation Displays
Can spatial auditory cues enable us to remain oriented while navigating real or virtual environments? Non-visual navigation interfaces are crucial for the blind, who suffer great reductions in mobility because of the difficulty of navigating new environments. Sighted users may also benefit from these types of displays when they are navigating but can’t see the screen of their mobile devi…
Sympathetic Guitar
Do humans response socially to abstract, expressive human-computer interfaces? To interact with the Sympathetic Guitar is to use a familiar and comfortable Western musical interface to feel an instant connection to musical culture and style of the East. The prototype senses guitarists’ hand motions and performance dynamics to augment a standard classical guitar with a digital drone…
Spatial Updating With(out) Physical Motions?
How important are physical motions for effective spatial orientation in VR? Most virtual reality simulators have a serious flaw: Users tend to get easily lost and disoriented as they navigate. According to the prevailing opinion, this is because physical motion cues are absolutely required for staying oriented while moving. In this study, we investigated how physical motion cues contribute …
Sonic Cradle
Sonic Cradle suspends the body is a completely dark chamber which encourages experiences comparable to mindfulness meditation. Users compose peaceful soundscapes in real-time using only their breathing. Introduction and demo of the Sonic Cradle Sonic Cradle is a relaxing human-computer interaction paradigm designed to foster meditative attentional patterns. The current p…
Projects
Beyond the Screen: Combating Cybersickness in Virtual Reality
This research delves into the pervasive issue of cybersickness, a major hurdle to widespread VR adoption. By gathering insights from a diverse group of VR experts, we identify the key factors contributing to motion sickness in virtual environments (aka cybersickness) and offer actionable strategies for developers, content creators, and researchers to build more comfortable and accessible VR experi...
Who Defines Embodiment? Cultural Bias in Interoceptive Wellness Technologies
If interoception is culturally learned rather than biologically universal, how should we design for this variability? Interoception—the perception of internal bodily states such as heartbeat, hunger, and emotion—is foundational to well-being. Despite its significance in wellness technologies within Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), existing designs often impose a universalized model of bo...
Compassionate Connection Oasis VR Toolkit (ccOasisVR)
Empowering Emerging Adults through Compassion and Enhanced Social Connection: Co-creating a Compassionate Connection Oasis VR Toolkit (ccOasisVR) Emerging adulthood (18-25) is a critical developmental phase, a tumultuous transition marked by heightened distress, and, unfortunately, a decreased likelihood that Emerging Adults (EAs) will seek support. The COVID-19 pandemic further exposed the urge...
Sensorium
This mixed-methods study investigates how real versus sham visual biofeedback influences subjective and physiological relaxation, self-connection, body awareness, flow, and self-transcendence within Sensorium 1.5 — an individual, immersive installation combining body-scan meditation, ambient sound, and HRV-responsive LED lighting. Fifty participants will experience both real and sham feedback in...
Being in Virtual Worlds
Being in Virtual Worlds: How Interaction, Environment, and Touch Shape Embodiment in Immersive Experiences Embodiment is an everyday experience that typically goes unnoticed. While we often take it for granted, with the adoption of virtual reality (VR) technology, embodiment in virtual bodies and worlds has become an important consideration for designers of immersive experiences. To date, the VR ...
HemisFear
HemisFear: A Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy Prototype Driven by Cross-Cultural Understanding of Dog Phobia Can virtual reality turn your terror of a barking stray into calm curiosity? HemisFear’s culturally attuned exposure therapy confronts dog phobias in both suburban backyards and bustling Indian streets, letting you practice handling real-life triggers with the safety of VR. Cynophobia, ...
BRieFLY - A meditative VR experience
Breathe, connect, and watch fireflies respond to your touch and breath BRieFLY is an exploratory VR prototype combining mindful breathing with playful interaction. This 6-minute meditative experience immerses users in a mixed reality environment where shimmering fireflies dynamically respond to their movements, as illustrated in the video below. The session begins with a 3-minute narrated b...
VR That Doesn’t Make You Sick: Understanding & Mitigating Cybersickness
Cybersickness remains a persistent challenge in VR/XR, hindering user experience and adoption. This course bridges research and industry, equipping developers, designers, and researchers with science-backed strategies to mitigate cybersickness through optimized locomotion, interaction, and environment design. Engage with case studies and activities to create more comfortable, accessible VR/XR expe...
Unleashing AI in the Classroom
How can AI tools like ChatGPT transform creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking in interdisciplinary education? And what are the risks of over-relying on AI tools in education, and how can students and educators navigate these challenges? How do students feel about using AI tools in their learning? What did they learn, and what would they do differently next time? Lessons Learned from Un...
Cybersickness Survey: Key Factors and Prevention/Reduction Strategies
Welcome to our research project on VR-induced motion sickness (aka cybersickness). We are exploring the factors that cause dizziness and nausea while using VR to make virtual reality experiences more comfortable for everyone — join our study today and be a part of research on combating cybersickness! Who Can Participate? We are looking for individuals who: Have over two years of experience...
Cybersickness & Benchmarking Tutorial at ISMAR 2024
Half-day tutorial at ISMAR 2024 on “Cybersickness: Understanding the Challenge and Building Solutions with Standardized Benchmarks” Join us for an in-depth exploration of cybersickness, a persistent challenge in virtual reality (VR). In this tutorial, we’ll delve into the causes and effects of cybersickness, drawing on the latest research and theories. We’ll...
1st International Workshop on Standardization in Cybersickness Research
1st International Workshop on Standardization in Cybersickness Research: “Establishing Standards for Cybersickness Measurement and Mitigation: A Community-Driven Approach” Date & time: Monday morning 8am-noon, 21 October 2024 at ISMAR 2024 Location: Redmond room, see ISMAR schedule Join remotely using this Zoom link or check on the ISMAR website for updates (contact us if you don't rec...
Pathways to flourishing
Leveraging Virtual Reality for cultivating compassion, resilience, social connectedness, and healthy habits in emerging adults facing chronic health challenges About half of youths with chronic physical conditions develop anxiety and/or depression, causing significant distress and disruption within their lives over many years. This underscores their need for well-being tools- particularly ones t...
Awedyssey: VR for promoting and enhancing well-being
We are investigating and creating a new virtual reality (VR) experience, 'Awedyssey', for the promotion and enhancement of well-being. Today, digital technology pervasively intersects with our daily lives, and VR stands out as a digital tool capable of fostering positive emotion like awe, self-transcendence, and authentic social connection. Connecting with nature is very important for our mental...
VR Sickness Benchmark System
Tackling VR Sickness: A Novel Benchmark System for Assessing Contributing Factors and Mitigation Strategies through Rapid VR Sickness Induction and Recovery Abstract This research introduces a novel VR sickness benchmark system, designed to address the lack of standardized tools for assessing and mitigating VR sickness. It aims to rectify the inconsistencies and limitations prev...
Multisensory Contributions Illusory Self-Motion (Vection)
Beyond the Eye: Multisensory Contributions to the Sensation of Illusory Self-Motion (Vection) Abstract Vection is typically defined as the embodied illusion of self-motion in the absence of real physical movement through space. Vection can occur in real-life situations (e.g., ‘train illusion’) and in virtual environments and simulators. The vast majority of vection research focuses on vectio...
InExChange
InExChange: Fostering Genuine Social Connection through Embodied Breath Sharing in Mixed Reality InExChange is an interactive mixed reality experience centering around an inflatable vest which conveys a physical sense of shared breathing on the diaphragm between two or more participants. The experience is composed of three acts in which the participants' breaths are transformed into metapho...
Designing with Biosignals Workshop at ACM DIS 2023
Designing with Biosignals: Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Directions for Integrating Physiological Signals in Human-Computer Interaction ABSTRACT Biosensing technologies are a rapidly increasing presence in our daily lives. These sensor-based technologies measure physiological processes including heart rate, breathing, skin conductance, brain activity and more. Researchers are exploring...
ETC - Embodied Telepresent Connection
Embodied Telepresent Connection (ETC): Exploring Virtual Social Touch Through Pseudohaptics ETC (Embodied Telepresent Connection) is an artistic VR project exploring ways of eliciting a feeling of embodied connection telepresently through pseudohaptics. This project emerged during the beginning of COVID-19-related lockdowns when our social interactions began to inhabit nearly exclusively virtual ...
Virtual Earthgazing
During months-long missions, Astronauts experience various aspects of social isolation and confinement. Our main aim is to study the feasibility of a virtual reality sensory stimulation augmentation called Virtual Earthgazing (VE). The VE experience is designed to elicit an “overview effect” of the Earth and induce the feeling of awe, which has been shown to expand time perception, increase e...
Flow
Flow is a prototype of a real-time interactive installation with Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) technology, aimed at evoking social connection through bio-signal sharing. The Muse™ headband would stream user’s EEG (brain wave) data and PPG (breathing) data into Unity 3D engine using LSL (Lab Streaming Layer). The generated visualization interact subtly with the participant's breathing pattern...
Synedelica
Reality - Reimagined Synedelica reimagines what is possible with immersive technology, providing a new perspective on reality. In this synesthetic mixed reality experience, visuals of the real world are modulated by sound, attuning immersants to the beauty hidden in the seemingly mundane. Synedelica shows the world in a new light, rekindling childlike wonder and encouraging exploration. ...
Autoethnographic Close Reading of Self-transcendent VR Experiences
Sipping the Virtual Elixir: An autoethnographic close reading of Ayahuasca Kosmik Journey a self-transcendent virtual experience. Recently self-transcendent experiences are gaining interest in the research community because of their ability to support wellbeing. Experiences of self-transcendence can be transformative, leading to a diminishment of self/ego and the feeling of unity with n...
Novel Cybersickness Measures and Countermeasures BoF
Novel Cybersickness Measures and Countermeasures: Birds of a Feather session at SIGGRAPH 2022 Interested in connecting & joining? If you're interested in connecting to others engaged or interested in the Novel Cybersickness Measures and Countermeasures, you could join our online interactive Birds of a Feather session at Siggraph 2022, on Fri Aug 05, 10 am-11:30 am Log in through h...
Telepresence
How can we improve telepresence systems (such as conference robots) so they are not just "zoom on wheels" but actually allow users to feel more present and navigate more easily around remote environments?" FeetBack: Augmenting Robotic Telepresence with Haptic Feedback on the Feet Telepresence robots allow people to participate in remote spaces, yet they can be difficult to manoeuvre with people ...
HyperJump flying to combat motion sickness
HyperJumping in Virtual Vancouver: Combating Motion Sickness by Merging Teleporting and Continuous VR Locomotion in an Embodied Hands-Free VR Flying Paradigm Motion sickness, unintuitive navigation, and limited agency are critical issues in VR/XR impeding wide-spread adoption and enjoyable user experiences. To tackle these challenges, we present HyperJump, a novel VR interface merging advantages ...
Design Strategies for Genuine Connection
There is a prominent interest in the potential of technology for mediating social connection, with a wealth of systems designed to foster the feeling of connection between strangers, friends, and family. In this project, we are exploring this design landscape to derive a transitional definition of mediated genuine connection and design strategies employed by artists and designers to support the f...
Concurrent locomotion and interaction in VR
Can more embodied and leaning-based interfaces help support concurrent locomotion and interaction in VR when physical walking isn't feasible? Physical walking is often considered the gold standard for VR travel whenever feasible. However, especially for larger-scale virtual travel the free-space walking areas are typically too small, thus requiring handheld controllers to navigate, which ...
SIRIUS - Virtual Earthgazing to mitigate effects of sensory isolation
SIRIUS (Scientific International Research in Unique Terrestrial Station) is a series of on-land isolation experiments modelling long-term spaceflight in order to assess the psychophysiological effects of isolation on a crew and prepare for long-duration spaceflights, such as a trip to Mars. An 8-month-long isolation study commenced in Moscow on Nov 4th, 2021, where a crew of 6 people (from Roscosm...
Leaning-based interfaces improve ground-based VR locomotion
Hand-held VR controllers are widely available and used, however they can contribute to unwanted side-effects, such as increased cybersickness, disorientation, and cognitive load. Here, we show how a leaning-based interfaces ("HeadJoystick") can help improve user experience, usability,and performance in diverse ground-based navigation including three complementary tasks: reach-the-target, follow-th...
Virtual Transcendent Dream
Flying dreams have the potential to evoke a feeling of empowerment (or self-efficacy, confidence in our ability to succeed) and self-transcendent experience (STE), which have been shown to contribute to an individual’s overall well-being. However, these exceptional dreaming experiences remain difficult to induce at will. Inspired by the potential of Virtual Reality (VR) to support profound emoti...
Breath of Light
One must first come to know, through observing oneself — just what one does with breathing. - Elsa Gindler Breath of light is a generative interactive installation, exhibited at the 13th Shanghai Biennale. The installation aims to foster a feeling of connection and awareness through the process of breathing synchronization. Each of the two participants generates their own light with their breat...
Integrating Continuous and Teleporting VR Locomotion into a Seamless "HyperJump" Paradigm
Here we propose a hybrid interface that allows user to seamlessly transition between a slow 'continuous' mode and a fast 'hyperjump' mode. The interface aims to maintain the immersion, presence, accuracy and spatial updating of continuous locomotion while adding the travel efficiency and minimizing the cybersickness. Continuous locomotion in VR provides uninterrupted optical flow, which mimics re...
VR Locomotion Interfaces Survey: How to Move in VR?
There are a multitude of different VR locomotion interfaces out there, all with their own pros and cons. In fact, far too many to all investigate in one behavioural study - so let's ask diverse VR experts for their opinion... Interested in supporting research on VR locomotion interfaces and helping the VR community better understand the pros and cons of different interfaces? We created a surve...
FaceHaptics: Robot Arm based Versatile Facial Haptics for Immersive Environments
Beyond audiovisual cues in VR: Using an HMD-mounted robot arm for versatile facial haptics Abstract: FaceHaptics is a novel haptic display based on a robot arm attached to a head-mounted virtual reality display. It provides localized, multi-directional and movable haptic cues in the form of wind, warmth, moving and single-point touch events and water spray to dedicated parts of the face ...
BioSpaceVR
Experience space like never before: An awe-inspiring VR experience that takes place in space where the Sun and stars react to biosensors. BioSpaceVR seeks to provide a virtual self-transcendent experience. Self-transcendent experiences are characterized by the feeling of unity with others and the world. Our project is a bio-responsive VR experience that creates an almost childlike experience of ...
Immersive Installation for Creative Expression and Public Performance: Transcending Perception
Artist Statement Transcending Perception is an interactive Virtual Reality (VR) installation developed by John Desnoyers-Stewart that allows participants to collaborate in the creative, improvisational production of multisensory experiences. Bodies and space are transformed into instruments which translate presence into performance. This installation reminds participants that they are cre...
Body RemiXer
Extending Bodies to Stimulate Social Connection in an Immersive Installation Body RemiXer connects bodies through movement. It is an experiential projection based Virtual Reality installation that explores novel forms of embodied interaction between multiple participants where their bodies mix into a shared embodied representation producing a playful interaction that aims to support the feeling o...
Lucid Loop: A Virtual Deep Learning Biofeedback System for Lucid Dreaming Practice
Can VR and neurofeedback deep learning art help enhance attention and lucid dreaming practice? Lucid dreaming, knowing one is dreaming while dreaming, is an important tool for exploring consciousness and bringing awareness to different aspects of life. We created a system called Lucid Loop: a virtual reality experience where one can practice lucid awareness via neurofeedback. Visuals are creativ...
Connecting through JeL – bio-responsive VR for interpersonal synchronization
Can a bio-responsive generative art installation foster interpersonal synchronization and connection? JeL is a bio-responsive, immersive, interactive, generative art installation designed to encourage physiological synchronization between the immersants. In this project, we will be exploring how novel forms of interaction can be included in immersive technology to foster the feeling of connection...
Embodied & Intuitive Flying for VR, Gaming, and TeleOperation
Flying has been a dream for mankind for millenia - but flying interfaces for VR, gaming, and teleoperation (e.g., drones) typically rely on cumbersome double-joystick/gamepads and do not allow for intuitive and embodied flying experiences. Here, we develop low-cost embodied flying interfaces that adapt leaning-based motion cueing paradigms thus freeing up hands for additional tasks beyond just na...
NaviBoard: Efficiently Navigating Virtual Environments
Here we propose a novel and cost-effective setup of a leaning-based interface ("NaviBoard") that allows people to efficiently navigate virtual environments - with performance levels matching the gold standard of free-space walking, without any increase in motion sickness Abstract Walking has always been the most common locomotion mode for humans in the real world. As a result, it has also been co...
3D User Interfaces Course
Siggraph 2018: 3D User Interfaces for Virtual Reality and Games: 3D Selection, Manipulation, and Spatial Navigation 3-hour Course Presented at Siggraph 2018 In this course, we will take a detailed look at different topics in the field of 3D user interfaces (3DUIs) for Virtual Reality and Gaming. With the advent of Augmented and Virtual Reality in numerous application areas, the need and interest...
VR/MR/AR 4 Good: Creating with a Purpose
Interested in connecting & joining? If you're interested in connecting to others engaged or interested in the xR4Good field, you could join the xR4Good facebook group, or fill out this online signup sheet and state what you're interested in Introduction Over the past five years, we have seen awareness and creation of Virtual, Mixed, and Augmented Reality (VR/MR/AR or, the ‘immersive realit...
Connected through "AWE": creating immersive experiences for social connection
Do you get enough “awe” in your life? In our busy day-to-day lives, we often take our experiences for granted. While we have the technology to connect with one another, like smart phones, we don’t necessarily get outside with nature, or stargaze. Such activities may consist of common awe-inspiring moments, and we now understand that feeling awe is associated with all sorts of social and well...
Navigation Interface Tutorial
Navigation Interfaces for Virtual Reality and Gaming: Theory and Practice First version held at IEEE VR 2017, Sunday, March 19, 1:30pm - 5:00pm, updated variants of the tutorial will be presented at ACM Chi 2018 (slides) and IEEE VR 2018. At The Spatial Cognition 2018 conference we will present a new tutorial on Spatial Navigation Interfaces for Immersive Environments focusing more on the...
Gamified Research
Gamifying Research - Researchifying Games While traditional experimental paradigms offer tight stimulus control and repeatability, then tend to be a bit boring and removed from many real-world situations, which can limit real-world transferability of results. How can we bring together the methodological strenghs of research with the intrinsic motivation of playfulness and gaming? The ...
Navigational Search in VR: Do Reference Frames Help?
Would the rectangular reference frame of a CAVE help to reduce disorientation and improve navigation performance in VR? Here, we show that simply providing the rectangular reference frame of a room (as a simple wireframe cuboid), but not a CAVE improved navigational search performance. Despite recent advances in virtual reality, locomotion in a virtual environment is still restricted becau...
Virtual Earthgazing - towards an overview effect in Virtual Reality
How can we use immersive VR to give people pivotal positive experiences without having to send them out into space? “We went to the Moon as technicians, we returned as humanitarians” reflected Edgar Mitchell after his space flight. This describes the overview effect – a profound awe-inspiring experience of seeing Earth from space resulting in a cognitive shift in worldview, le...
Lean and Elegant Motion Cueing in VR
How do we best design locomotion interfaces for VR that provide "enough" physical motion cues (vestibular/proprioceptive) while still being effective, affordable, compact, and safe? Despite amazing progress in computer graphics and VR displays, most affordable and room-sized VR locomotion interfaces provide only little physical motion cues (e.g., vestibular & proprioceptive cues). To provide...
Pulse Breath Water
Pulse Breath Water is an immersive virtual environment manipulated by the pulse of a participant’s breath that provokes and challenges the interaction between a user and the substantial element of the environment: water. The system “senses” the participant, while the participant’s breathing feeds the system. The process is a symbiotic play between internal human processes [biosensing t...
Lost Spirit
Flight after death: Lost Spirit is an experiential-based Virtual Reality (VR) game whereby the player is transported into the spirit world as they take flight to the afterlife. Experience flight, weightlessness, and wonder. In Lost Spirit, you are stuck in the limbo - a world between the living and the dead. You will drift and fly through different environments, each corresponding to different...
Immersive & Embodied Teleoperation Interfaces
Developing virtual interfaces for embodied tele-operation and locomotion. How can we best design and implement an embodied telepresence system for tele-robotics, so we can safely explore remote, hard-to-reach, or potentially hazardous areas or situations? The goal of the "TeleSpider" project is to design and implement a telepresence system where users can remotely operate a robotic spid...
state.scape: EEG-based Responsive Art Installation
State.scape: Using EEG-based brain-computer interfaces for a responsive art installation State.scape is an interactive installation in which audio-visuals are generated from users affective states (engagement, excitement, and meditation). The installation relies on a brain-computer interface based virtual environment and sonification, which both served as a platform for the exploration of users�...
Biofeedback in VR - SOLAR
Resonance in Virtual Environments: hacking biofeedback for altering user's affective states How can we combine immersive virtual environments (VE) with biofeedback and gamification to foster relaxation, de-stressing and meditative states? That is, instead of increasing sensory overload, can we use the immersive and affective potential of VE and gamification to assist especially novice meditato...
Motion Seats for VR
Using motion seats for enhancing locomotion and immersion in VR How can we provide a "moving experience" through VR without having to use a full-scale motion platform? Could a compact and relatively low-cost "motion seat" provide some of the same benefits, thus reducing cost, complexity, space & safety requirements? Despite considerable advances in Simulation and Virtual Real...
VR in Architecture Design & Review
How can we use immersive Virtual Reality and embodied locomotion interfaces to to design more cost- and space-efficient solutions for effective presentation and communication of architectural designs and ideas? Our overall goal is to iteratively design and evaluate a novel embodied VR system that enables users to quickly, intuitively, and precisely position their virtual viewpoint in 3D space...
Transition into VR: TransLocation
How can we ease users' transition from the real surroundings into the virtual world? Many of today’s virtual reality (VR) setups are very much focused on technical aspects rather then the benefits of a coherent user experience. This work explores the idea of enhancing the VR experience with a transition phase. On a physical level, this transition offers the user a meaningful metaphor for en...
Cross-Disciplinary 'Immersion' Framework
Describing media as 'immersive' is ambiguous. From debilitating addiction to therapeutic relief, media engagement holds a clear duality in its effect on humanity... Without an interdisciplinary characterization of "immersion", why do we allow this concept to be so readily invoked in discussions of books, visual art, video games, virtual reality systems and more? While "immersion" into tradit...
The Tabletop Makerspace
The tabletop Makerspace was a Mitacs internship project conducted in collaboration with Science World. A set of classroom tools was developed to support ‘Maker’ activities at the museum. The tools included a home-built 3D printer and a set of electronics kits for working with the Arduino microcontroller. An introduction to electronics workshop was developed with local makers and Science World ...
Gyroxus Gaming Chair for Motion Cueing in VR
Can self-motion perception in virtual reality (VR) be enhanced by providing affordable, user-powered minimal motion cueing? Introduction & Motivation: Can self-motion perception in virtual reality (VR) be enhanced by providing affordable, user-powered minimal motion cueing? To investigate this, we compared the effect of different interaction and motion paradigms on onset latency and intensi...
Embodied Self-Motion Illusions in VR
How can we provide humans with a believable sensation of being in and moving through computer-generated environments (like VR, computer games, or movies) without the need for costly and cumbersome motion platforms or large free-space walking areas? That is, how can we "cheat intelligently" by providing a compelling, embodied self-motion illusion ("vection") without the need for full physical mo...
Dynamic Visual Cues for Spatial Updating
Why is object recognition from novel viewpoints facilitated if not the object rotates, but the observer moves around the object? According to the prevailing opinion, "spatial updating" of our mental spatial representation is supposed to be the underlying process. Here, we provide first evidence that challenge this notion, in that dynamic visual cues alone might be sufficient or at least contrib...
Navigational Search in VR: Do we need to walk?
Do we need full physical motions for effective navigation through Virtual Environments? Recent results suggest that translations might not be as important as previously believed, which could enable us to reduce overall simulation effort and cost Physical rotations and translations are the basic constituents of navigation behavior, yet there is mixed evidence about their relative importance for co...
Spatial Cognition in VR vs. real world
Comparing spatial perception/cognition in real versus immersive virtual environments: it doesn't compare! Virtual reality (VR) is increasingly used in psychological research and applications – but does VR really afford natural human spatial perception/cognition, which is a prerequisite for effective spatial behavior? Using judgment of relative direction (JRD) tasks, Riecke & McNamara (Psychonom...
iSpaceMecha
Collaboration between the iSpace lab at SIAT and Mechatronics Undergraduate Interns to design and build a unique, virtual reality multi-modal motion simulator The iSpace program is centered on investigating what constitutes effective, robust, and intuitive human spatial orientation and behaviour. This fundamental knowledge will be applied to design novel, more effective human-computer interfaces ...
Path Integration in 3D
Switching Spatial Reference Frames for Yaw and Pitch Navigation: We're used to navigating on the ground plane, and have developed specific strategies to do so. How do these change if we move in a vertical plane (roller-coaster-like, including head over heels motions)? Can we still maintain orientation and remember where we came from, even though such upwards or downwards (pitch) motions are less ...
Auditory Navigation Displays
Can spatial auditory cues enable us to remain oriented while navigating real or virtual environments? Non-visual navigation interfaces are crucial for the blind, who suffer great reductions in mobility because of the difficulty of navigating new environments. Sighted users may also benefit from these types of displays when they are navigating but can't see the screen of their mobile devi...
Sympathetic Guitar
Do humans response socially to abstract, expressive human-computer interfaces? To interact with the Sympathetic Guitar is to use a familiar and comfortable Western musical interface to feel an instant connection to musical culture and style of the East. The prototype senses guitarists' hand motions and performance dynamics to augment a standard classical guitar with a digital drone...
Spatial Updating With(out) Physical Motions?
How important are physical motions for effective spatial orientation in VR? Most virtual reality simulators have a serious flaw: Users tend to get easily lost and disoriented as they navigate. According to the prevailing opinion, this is because physical motion cues are absolutely required for staying oriented while moving. In this study, we investigated how physical motion cues contribute ...
Sonic Cradle
Sonic Cradle suspends the body is a completely dark chamber which encourages experiences comparable to mindfulness meditation. Users compose peaceful soundscapes in real-time using only their breathing. [vimeo 35764652] Introduction and demo of the Sonic Cradle Sonic Cradle is a relaxing human-computer interaction paradigm designed to foster meditative attentional patterns. The current p...